Setting Up Public Load Balancer On Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- Load Balancer enables Automated traffic distribution
- Load Balancer Improves resource utilization, facilitates scaling, and helps ensure high availability
- There are two types public and private
Design
Lets provision the following Infrastructure.
For the sake of simplicity lets focus only on the highlighted items.

Prerequisites
SSH
Make sure to generate the SSH key Pair, ignore if already done
Implementation
We need the following
- VCN
- Internet Gateway
- Two subnets for two Load Balancers
- One security list for LB Subnets
- One Route table for LB Subnets
- Load Balancers
- Two compute instances
- one subnet, security list, route table for backendset (Compute instances)
Creating VCN
Lets create VCN, and name it public_lb_vcn.
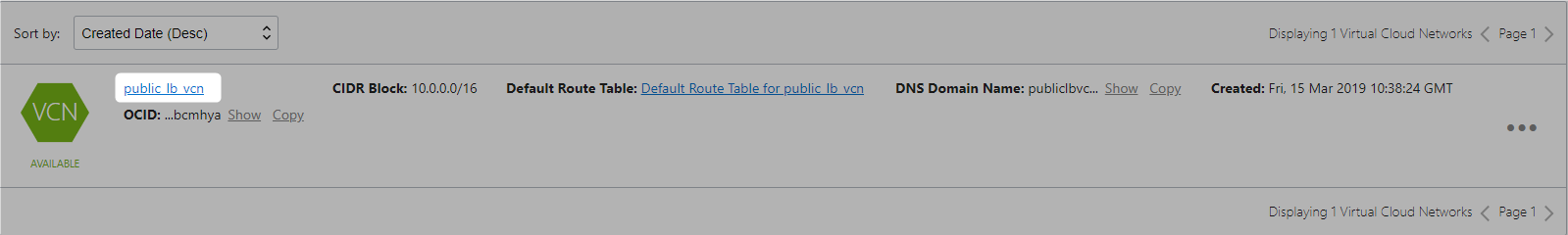
Since we have created above vcn with option “Create Virtual Cloud Plus Related Resources” it would create the following automatically.
- Subnets
- Rout Table
- Internet Gateway
- Security List and
- DHCP Options
Will try to reuse some of it where ever applicable instead of creating new one.

Create New Security List for Loadbalancer
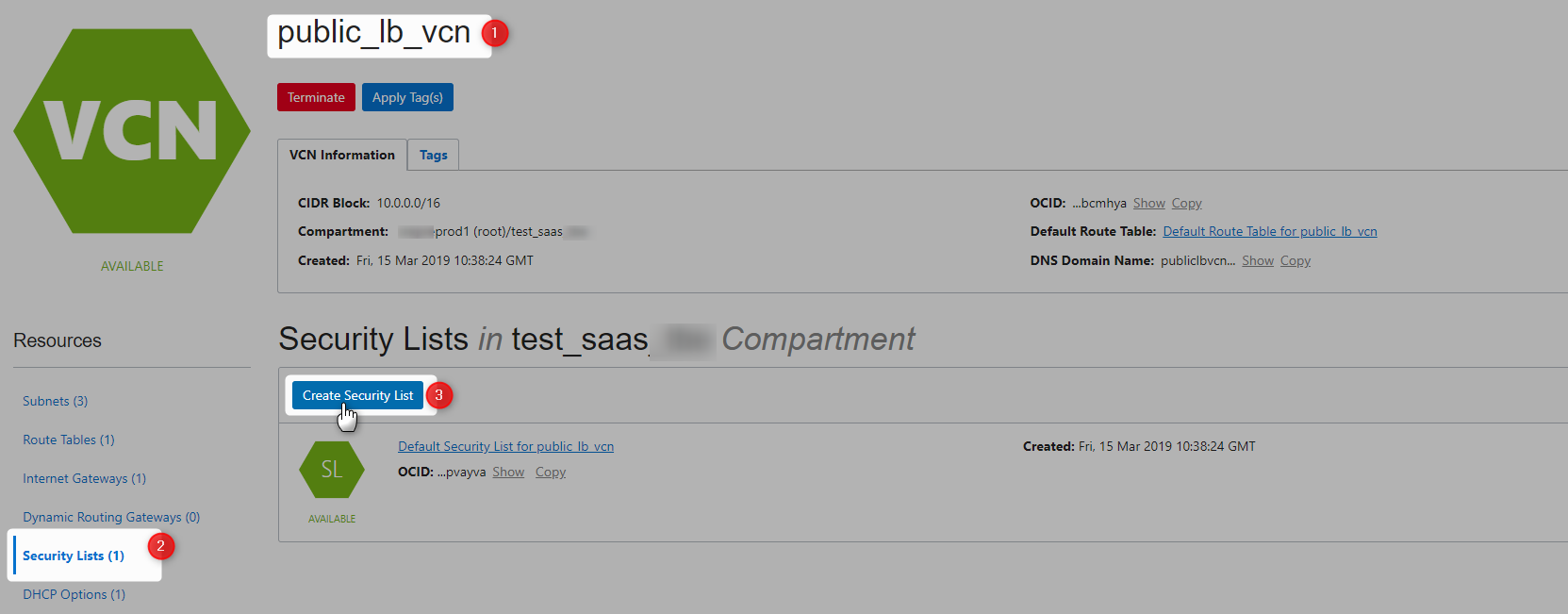


Refer this for more details on SecurityList
Crete New Route Table For Loadbalancer

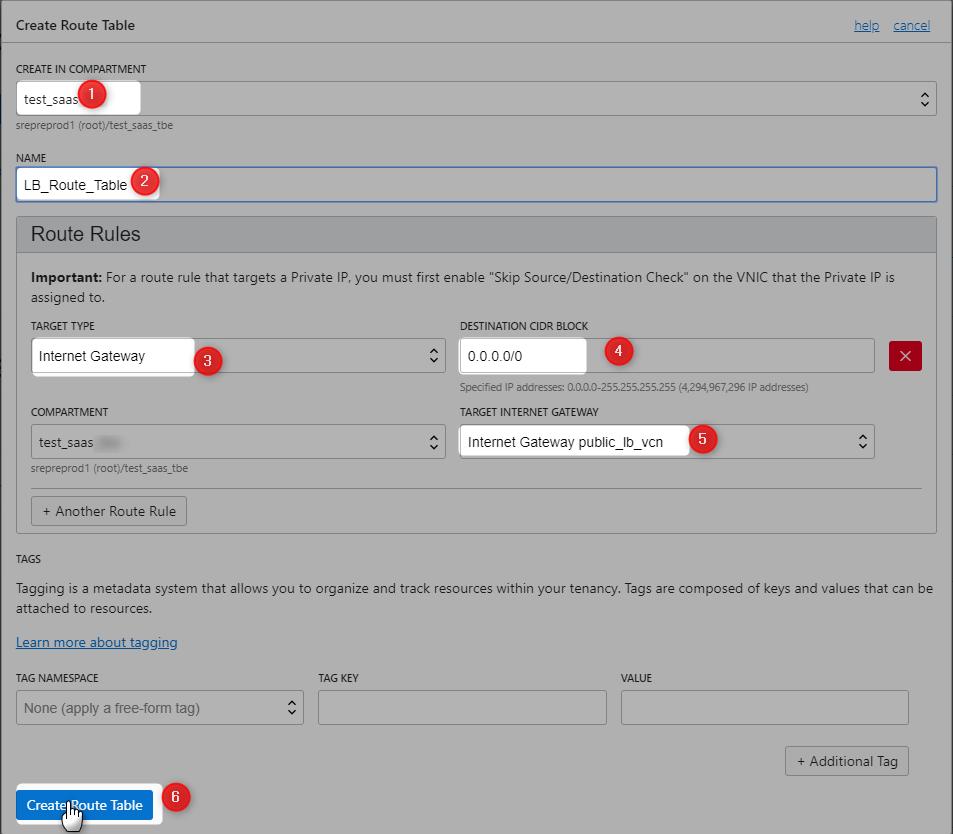
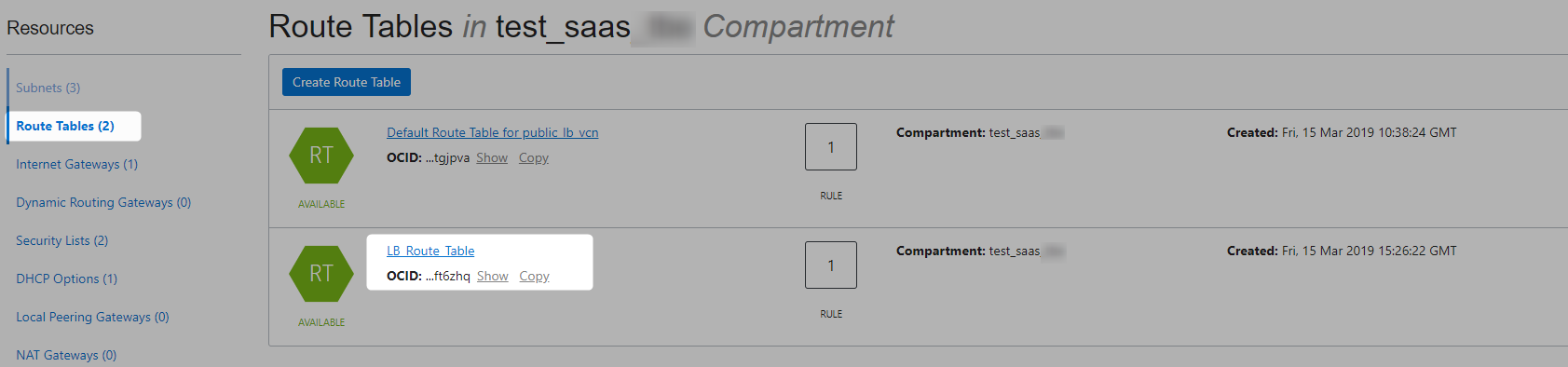
Refer this for more details on Routers
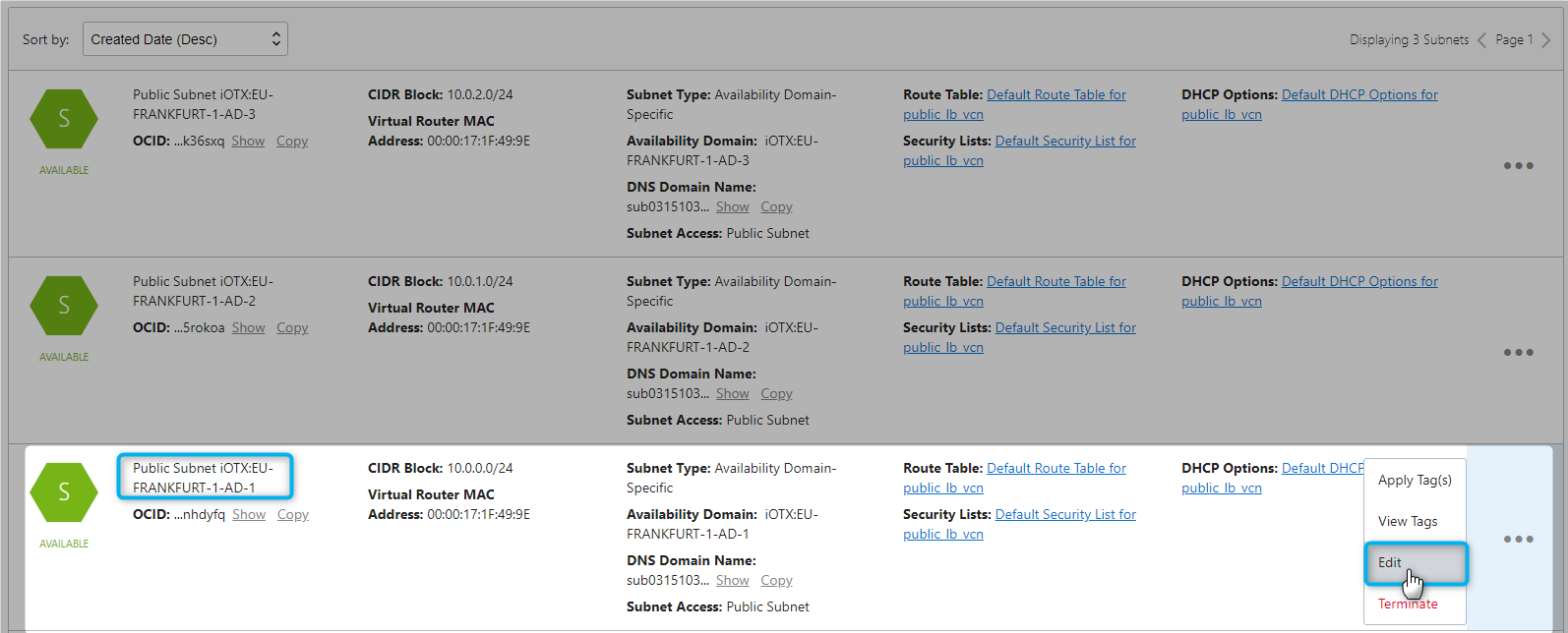
Modify Existing Subnets
Will reuse existing 3 subnets from public_lb_vcn for this purpose
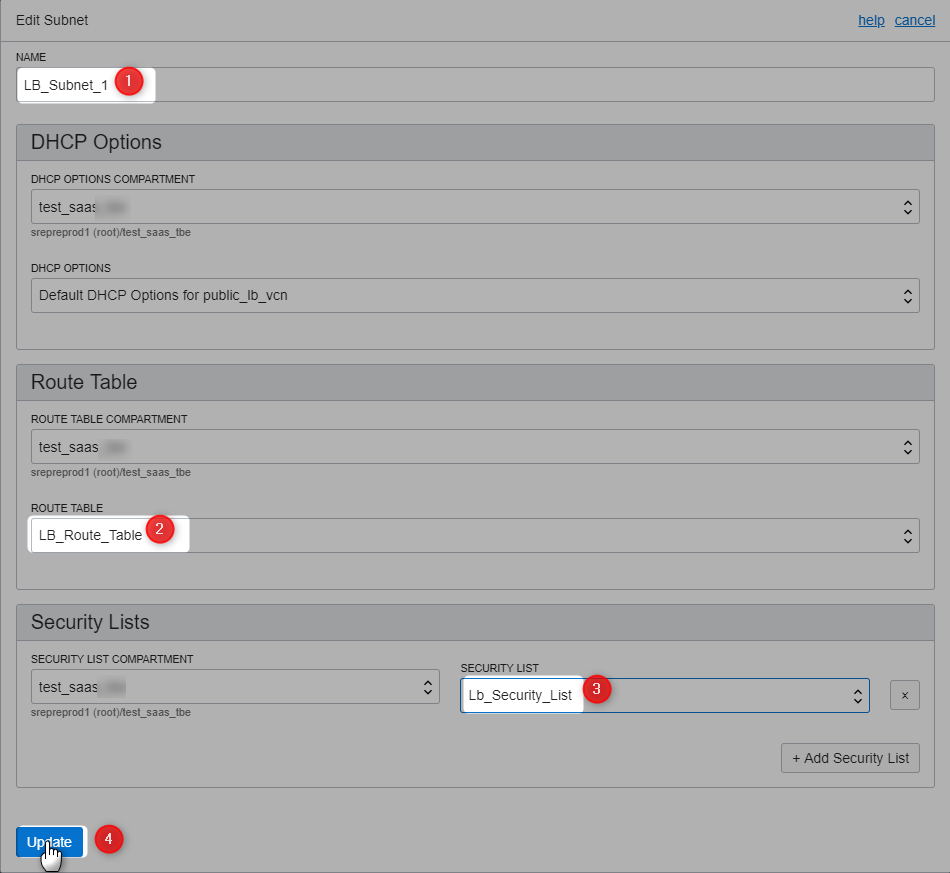
AD-1 (LB_Subnet_1)
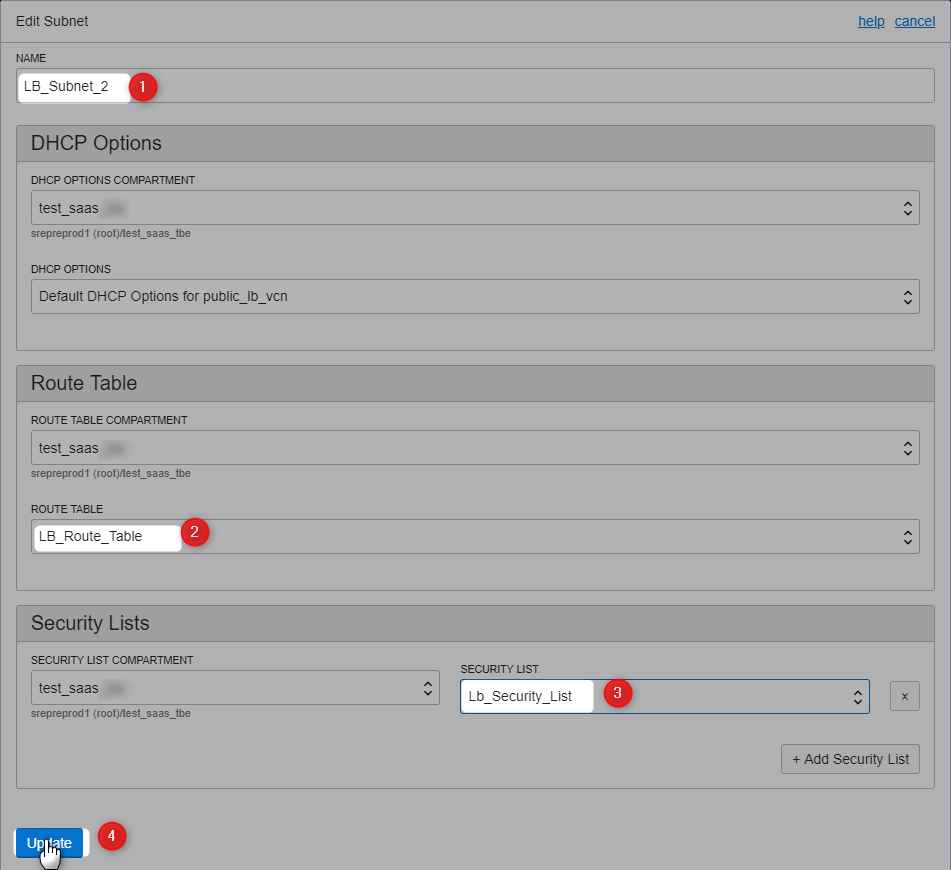
AD-2 (LB_Subnet_2)
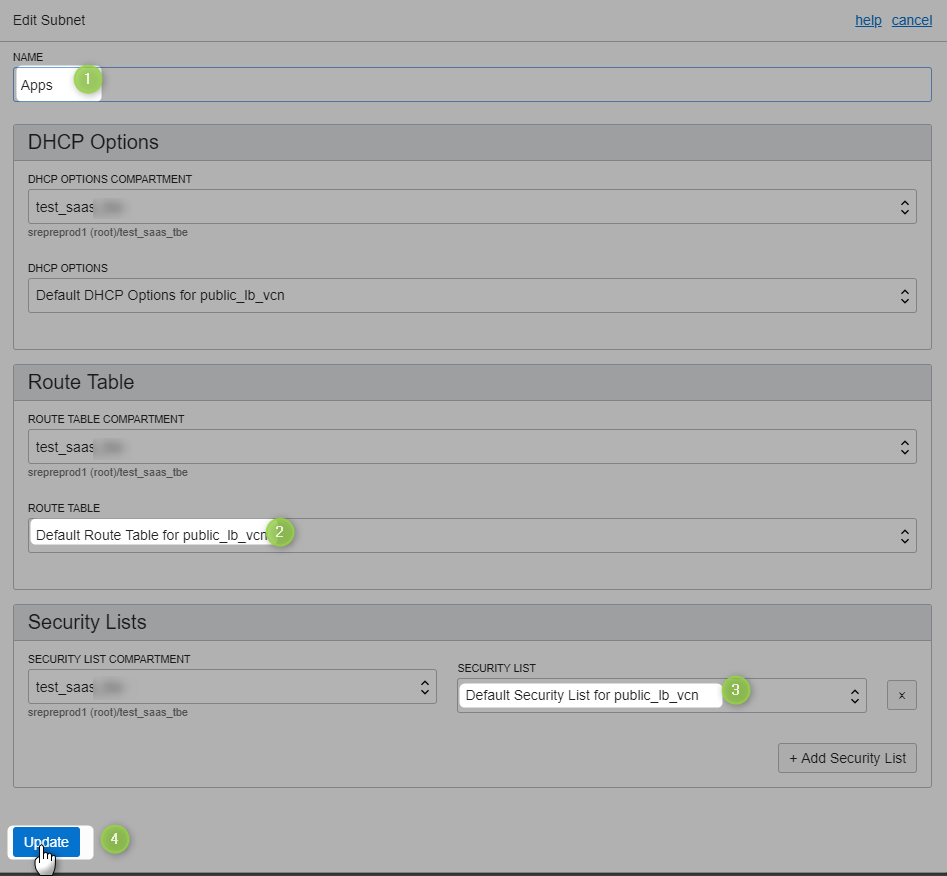
AD-3 (Apps)
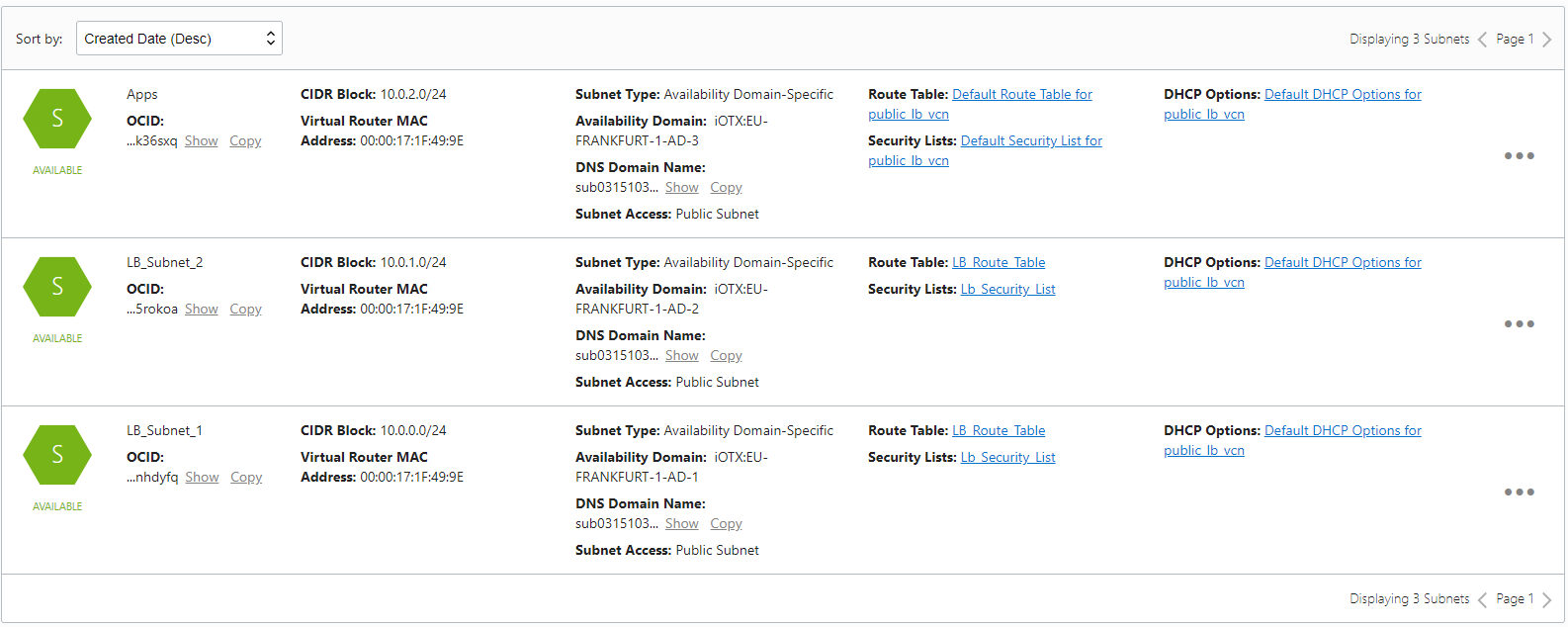
All Subnets
Here are the updated subnets
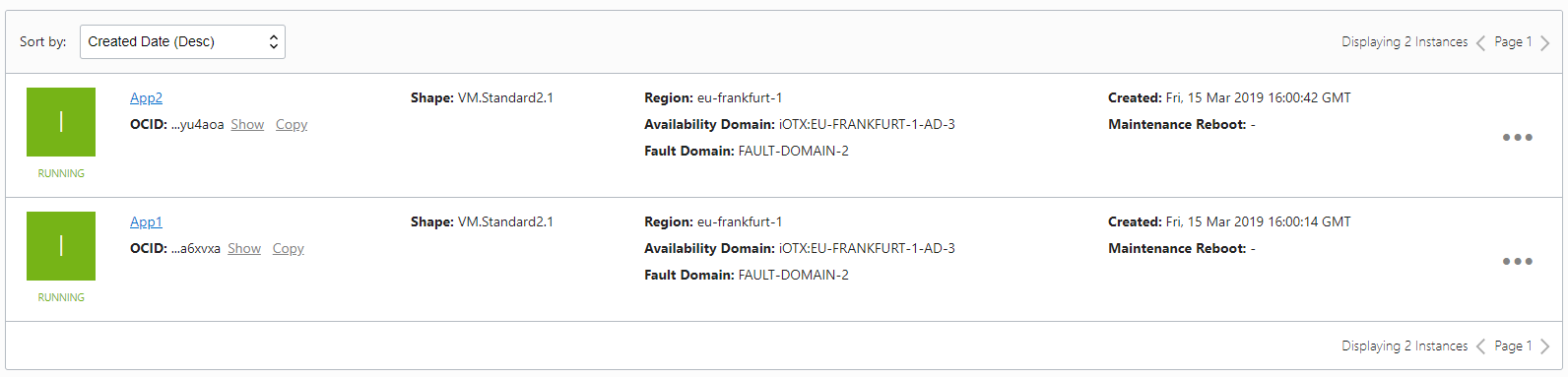
Create Two App Compute Instances
Create two compute instances and do the following :
- Install Apache
- Firewalls opened to allow HTTP
- Create index.html
Follow the steps in Create Compute Instance, to create two compute instances.
Refer this for more details on Compute Service
App1
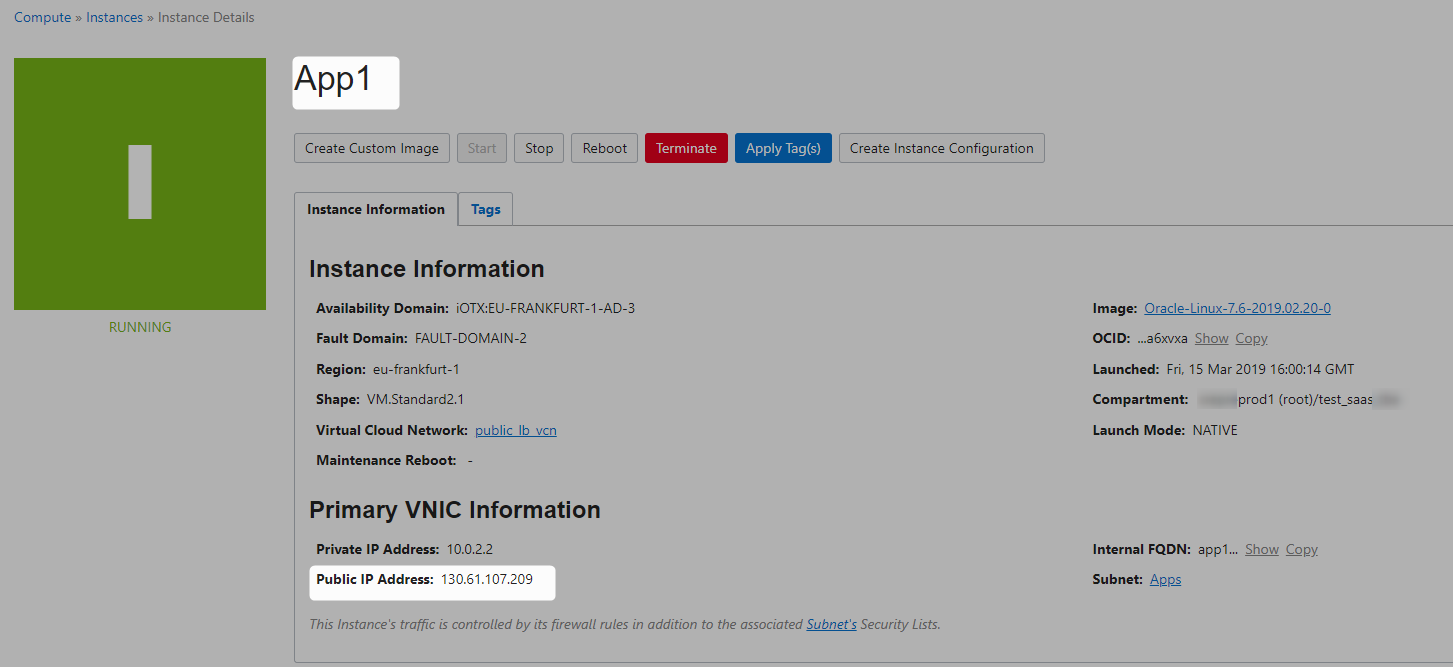
Lets connect
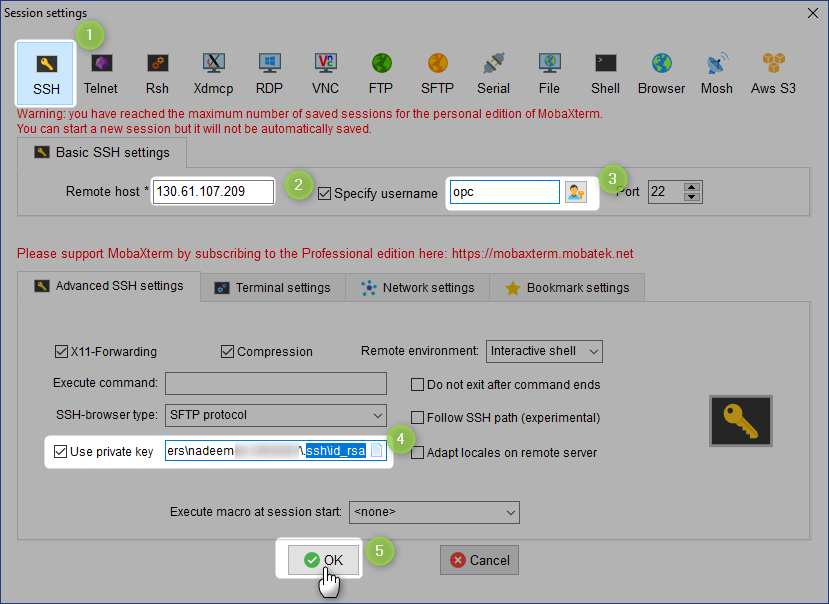
Install Apache on App1
Install HTTP Server
sudo yum install httpd -y
Start Apache server
sudo apachectl start
Configure it to start after system reboot
sudo systemctl enable httpd
Quick Check on configurations
[opc@app1 ~]$ sudo apachectl configtest
Syntax OK
[opc@app1 ~]$
Create firewall rules to allow access to the ports on which the HTTP server listens.
[opc@app1 ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
success
[opc@app1 ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
success
[opc@app1 ~]$
Create Index file for App1
sudo bash -c 'echo This is App1 running on OCI >> /var/www/html/index.html'
[opc@app1 ~]$ curl localhost
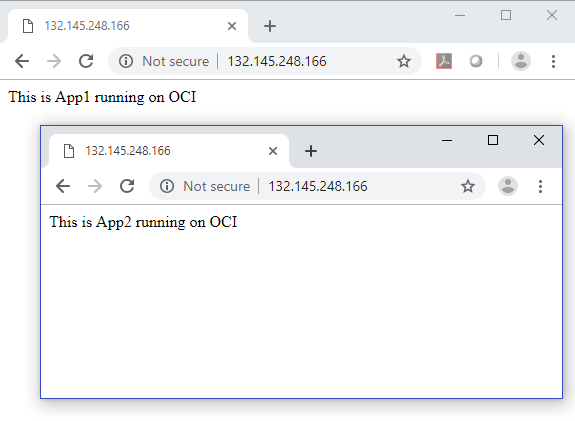
This is App1 running on OCI
[opc@app1 ~]$
App2
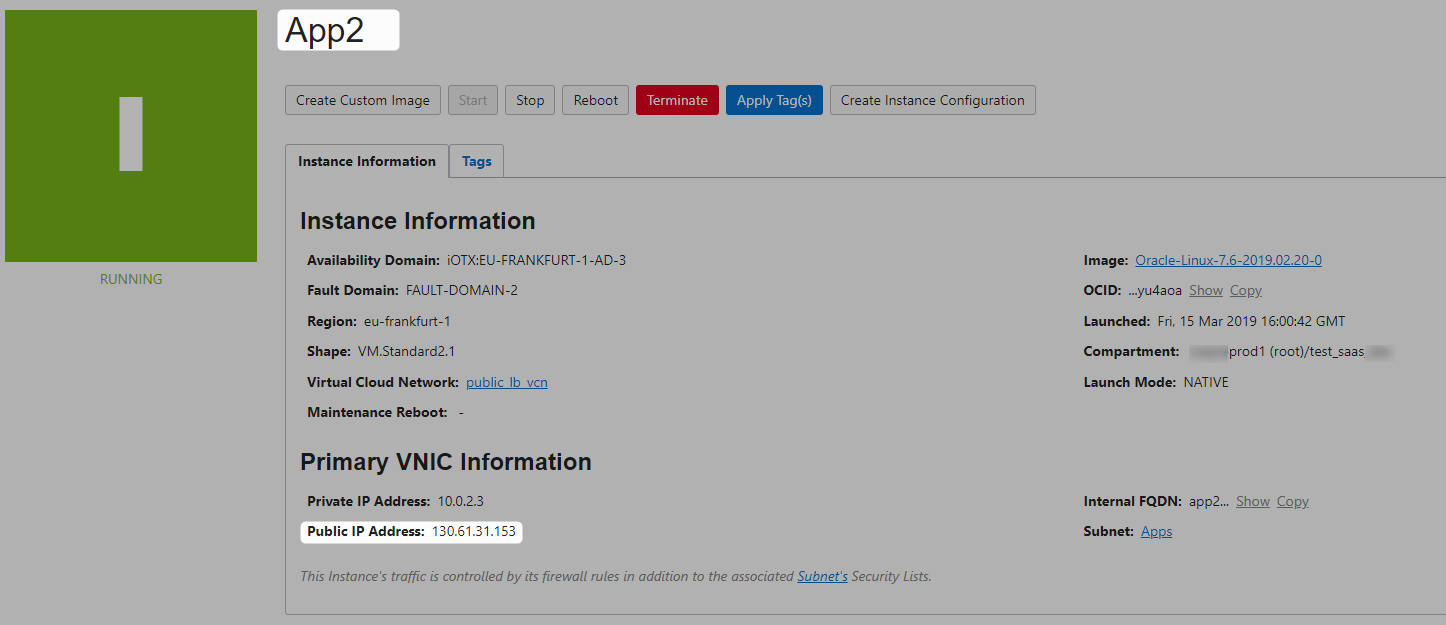
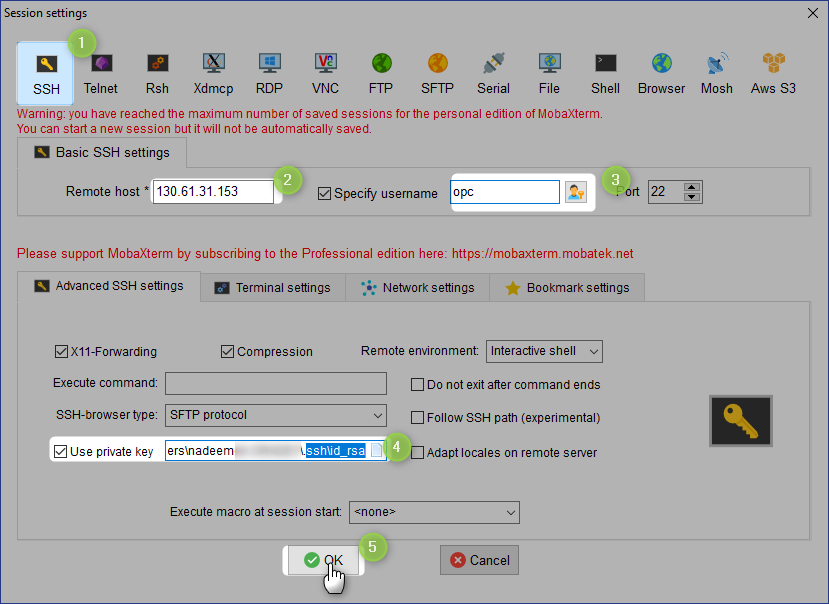
Install Apache on App2
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo yum install httpd -y
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo apachectl start
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo systemctl enable httpd
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo apachectl configtest
Syntax OK
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
success
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
success
[opc@app2 ~]$ sudo bash -c 'echo This is App2 running on OCI >> /var/www/html/index.html'
[opc@app2 ~]$ curl localhost
This is App2 running on OCI
[opc@app2 ~]$
Create Load Balancer

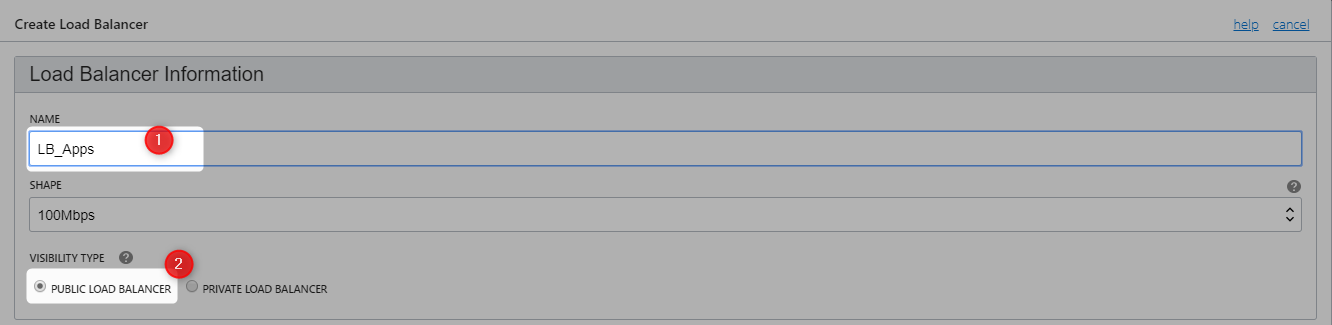
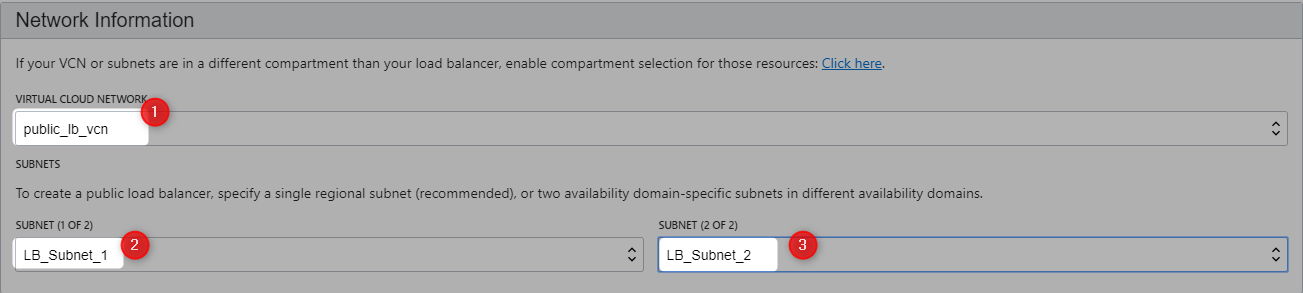

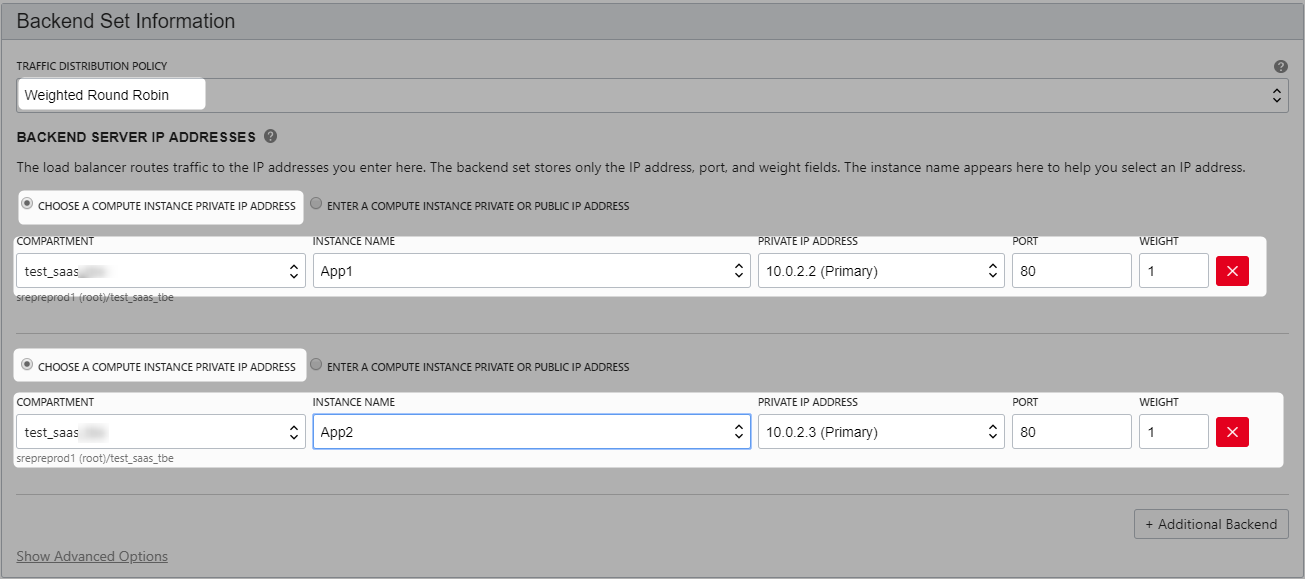
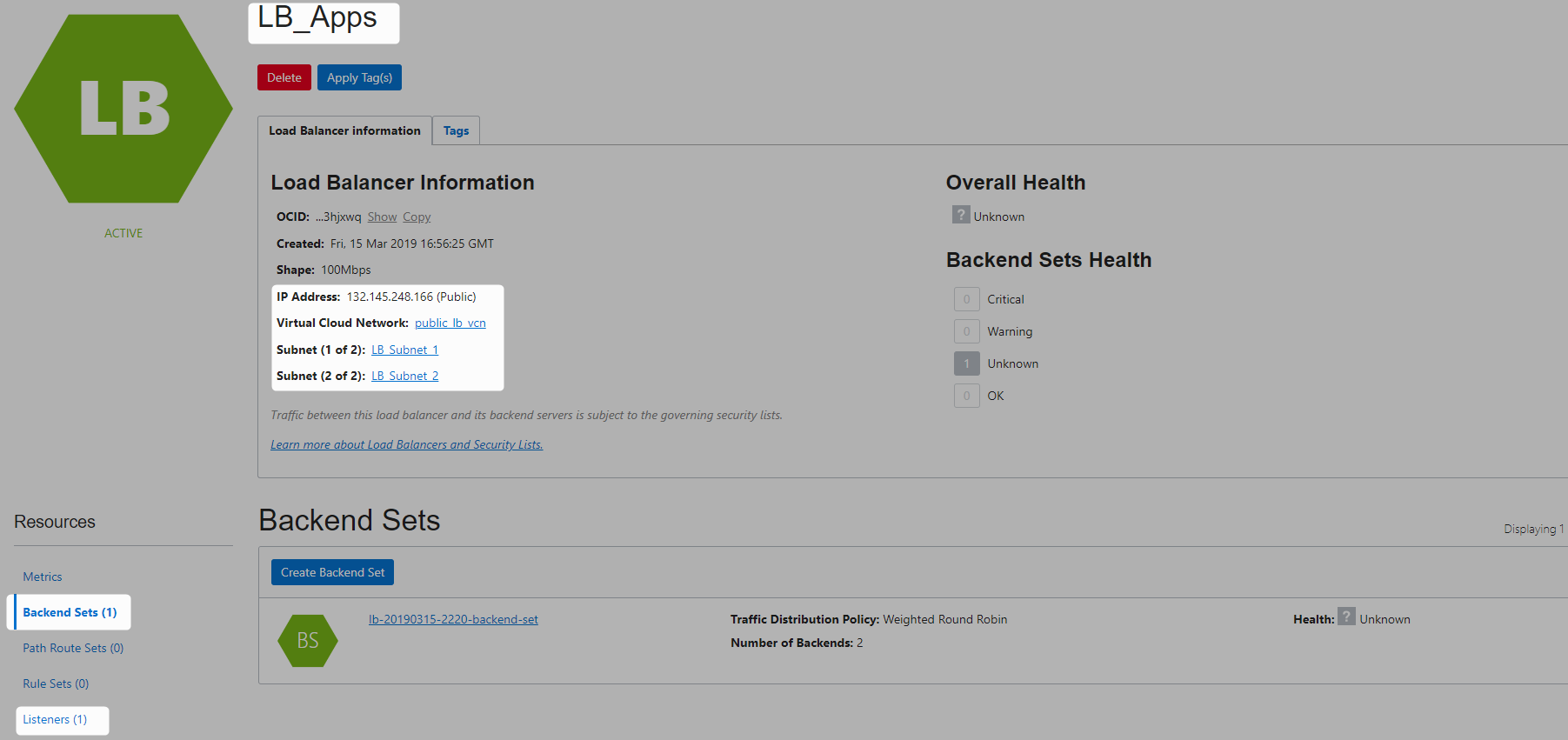
When a load balancer is created, you’re assigned a public IP address to which you route all incoming traffic.
The IP address is highly available, meaning it is available from both subnets that you specified.
Note that it is only active in one subnet at a time.
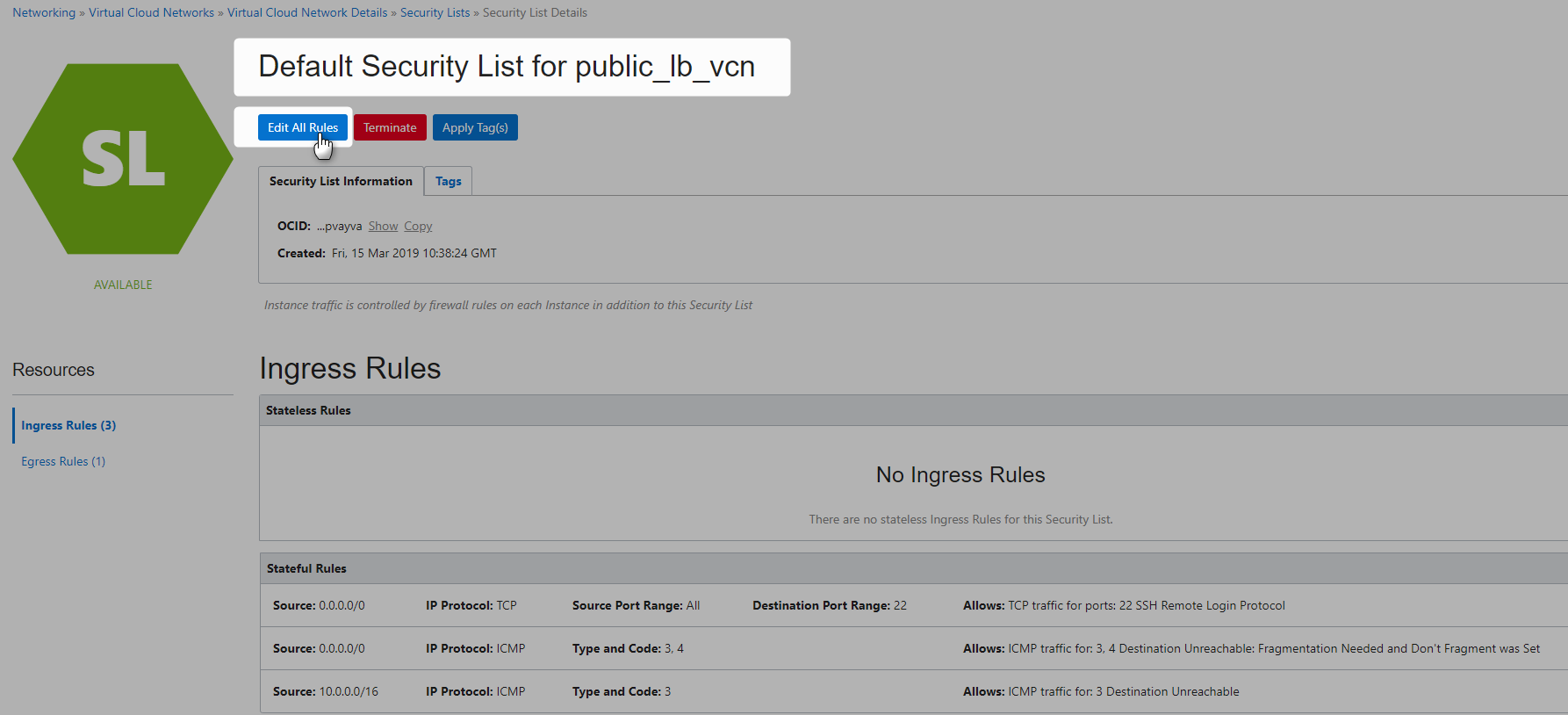
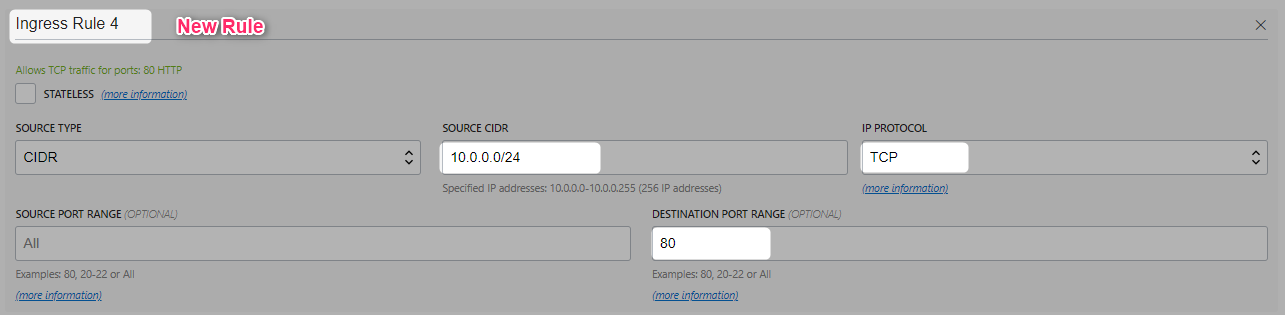
Update SecurityList
Update LB_Security_List to allow internet traffic to listener.

You would be updating both ingress and egress.

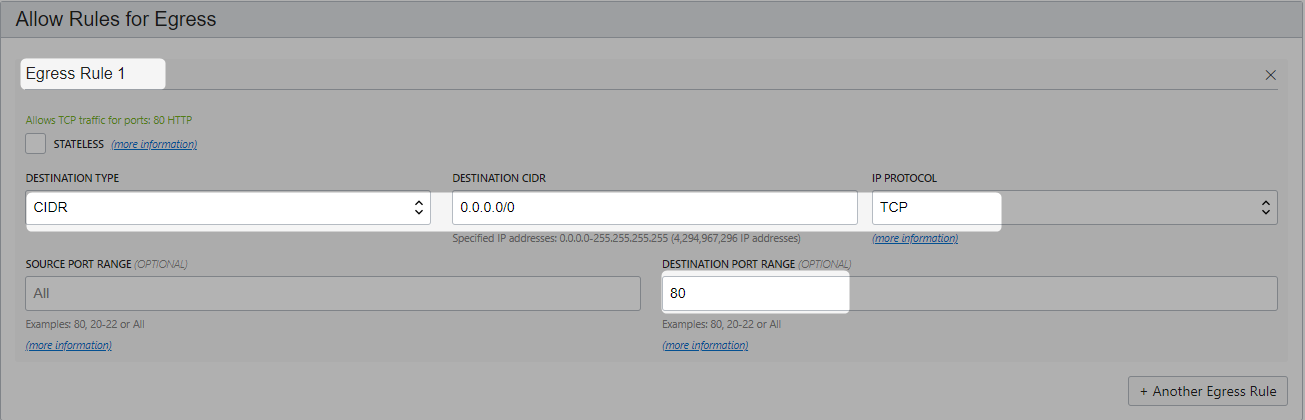
Update Default Security List to allow traffic from Load balancers to Apps
Subnet 1
Subnet 2

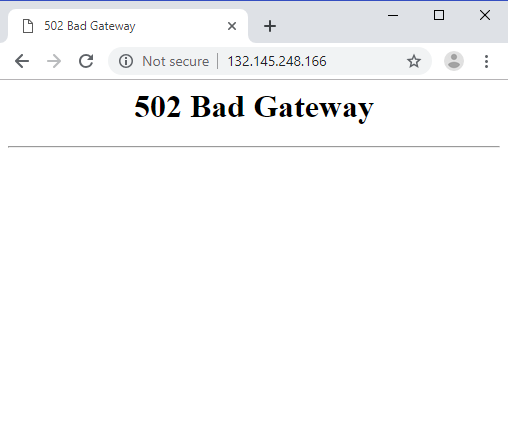
Testing
If you get 502 wait for some more time.
After some times it works
Clean Up
Locadbalancer
Terminate the load balancer


Compute Instance
Terminate the two compute instances. Refer this for more details on how to terminate Compute instance.
VCN
Termincate the VCN. Refer this for more details on how to terminate VCN.